One Of The Best Info About How To Increase Tidal Volume

The ‘tidal volume challenge’ is a novel test proposed to improve the reliability of ppv during low tidal volume ventilation.
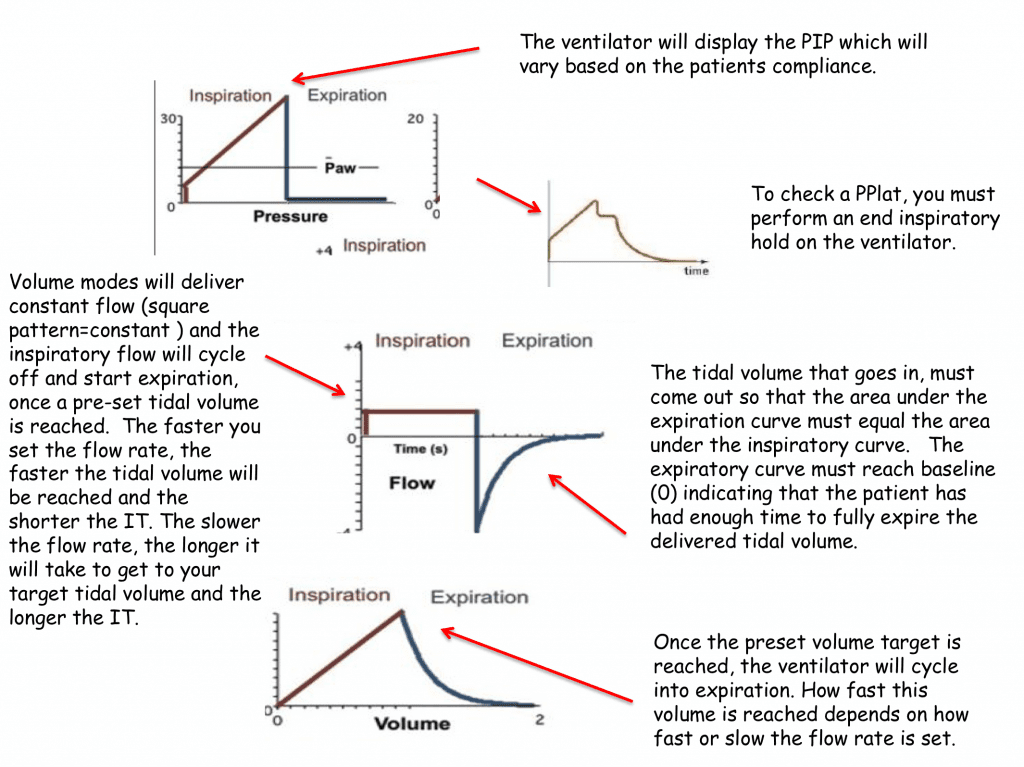
How to increase tidal volume. The present paper illustrates the physiological effects of delivering a tidal volume to the lungs of patients with ards, and suggests an approach to tidal volume. They may benefit from increasing the set pressure support. Set the rate, tidal volume, fio2, peep.
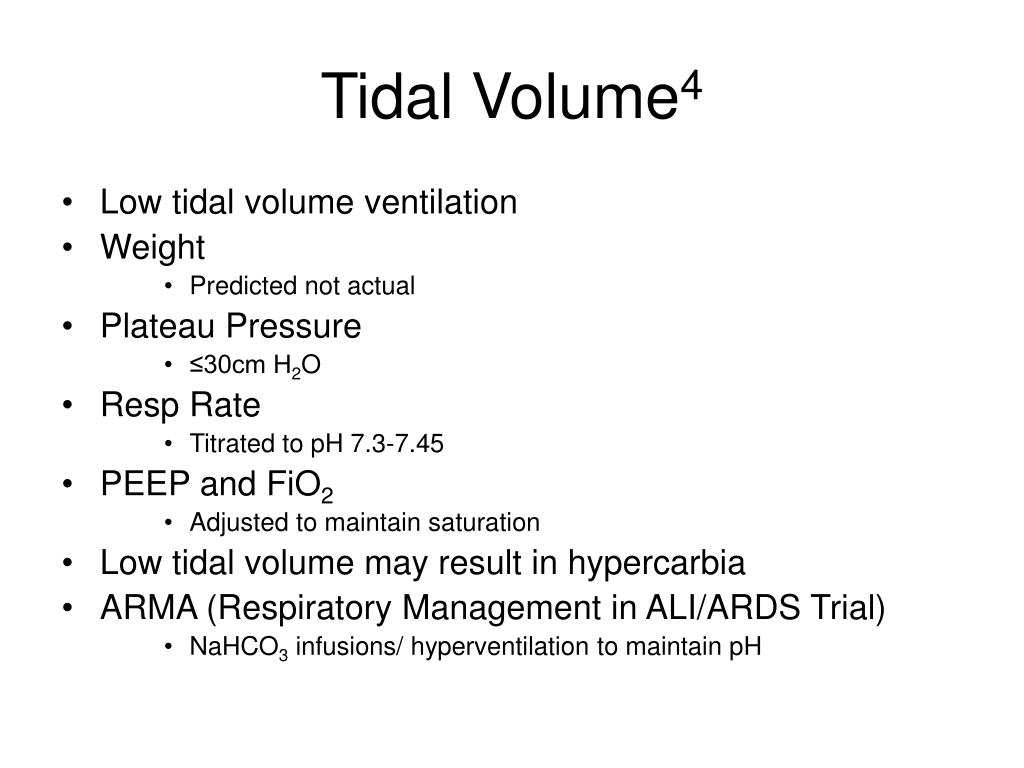
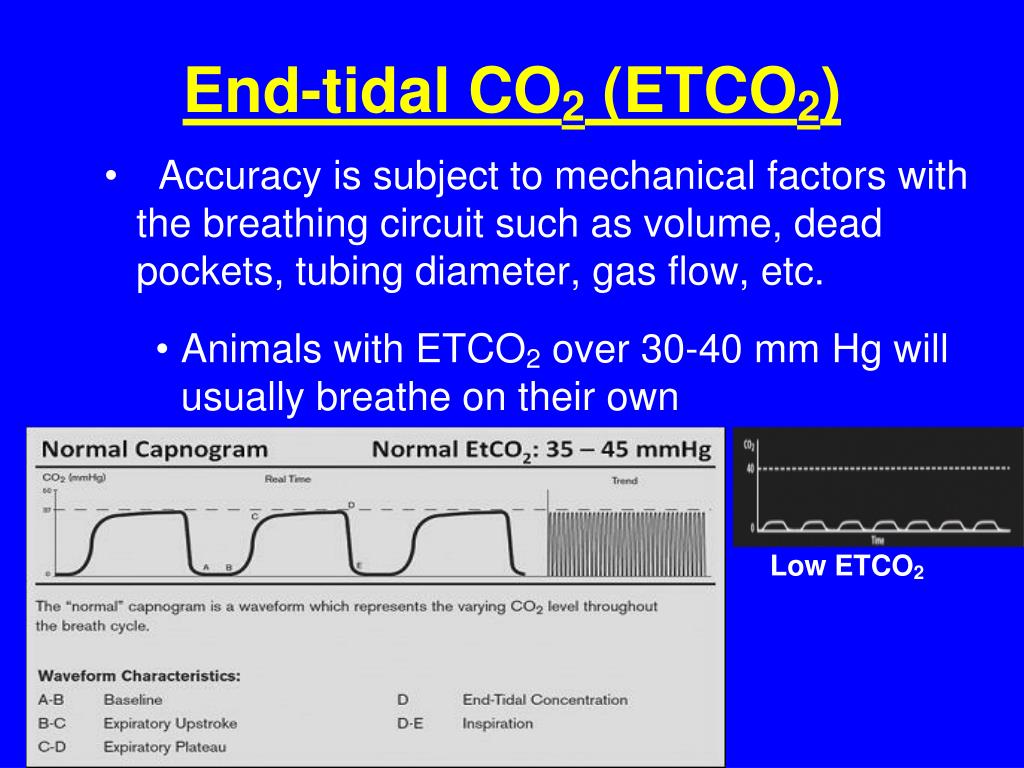
These technical advancements have impact on clinical. Tidal volume is the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle. To assess for adequate ventilation, or removal of co2, check the patient’s arterial carbon dioxide levels (paco2 ) on an arterial blood gas (abg).
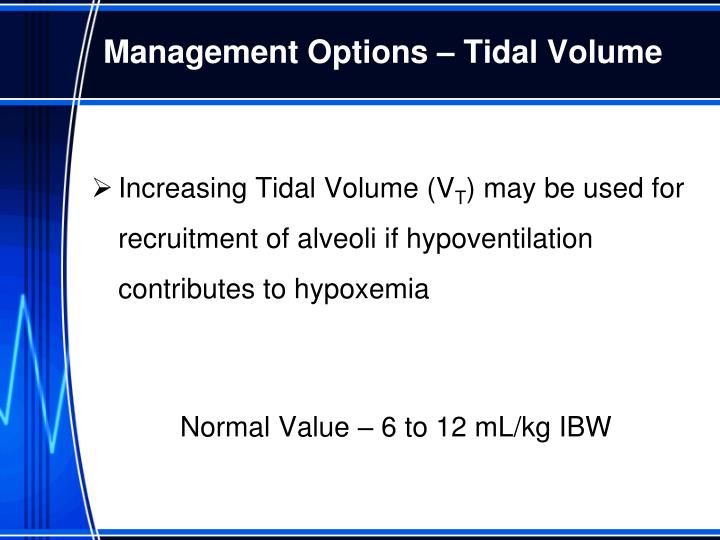
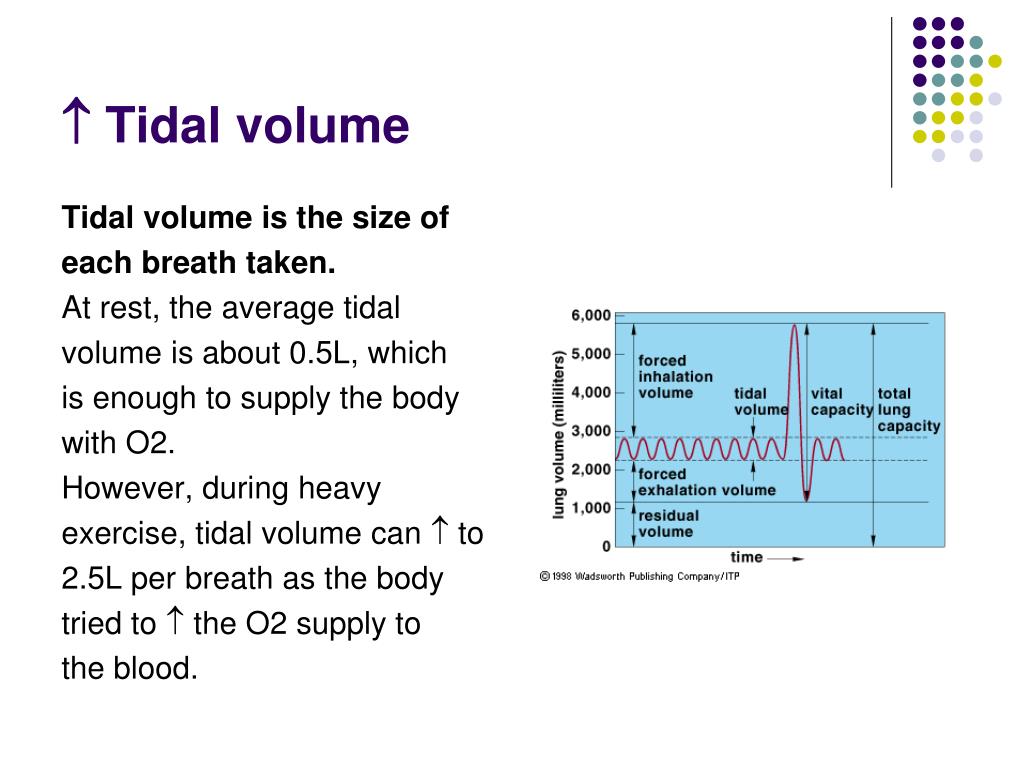
Importance of tidal volume in respiratory. It is a vital clinical parameter that allows for. It measures around 500 ml in an average healthy adult male and approximately 400 ml in a healthy female.
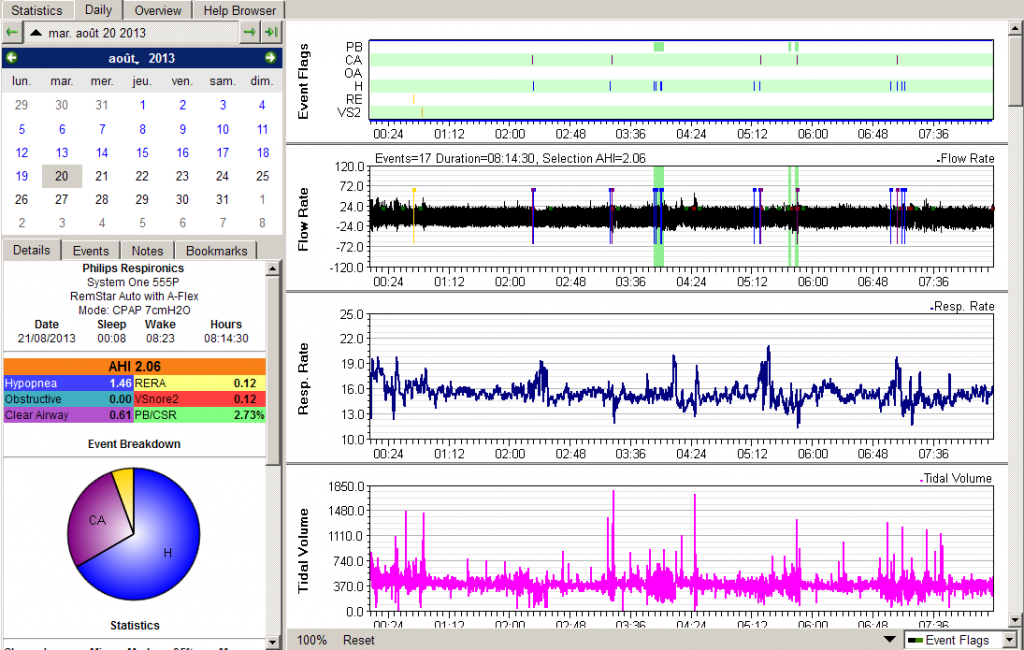
Volumes must be continuously monitored to ensure they are enough to effectively ventilate your patient, but not too high that they cause damage. Anatomy | physiology tidal volume by admin september 3, 2023 table of contents what is a tidal volume? Tidal volume is vital when it comes to setting the ventilator in critically ill patients.
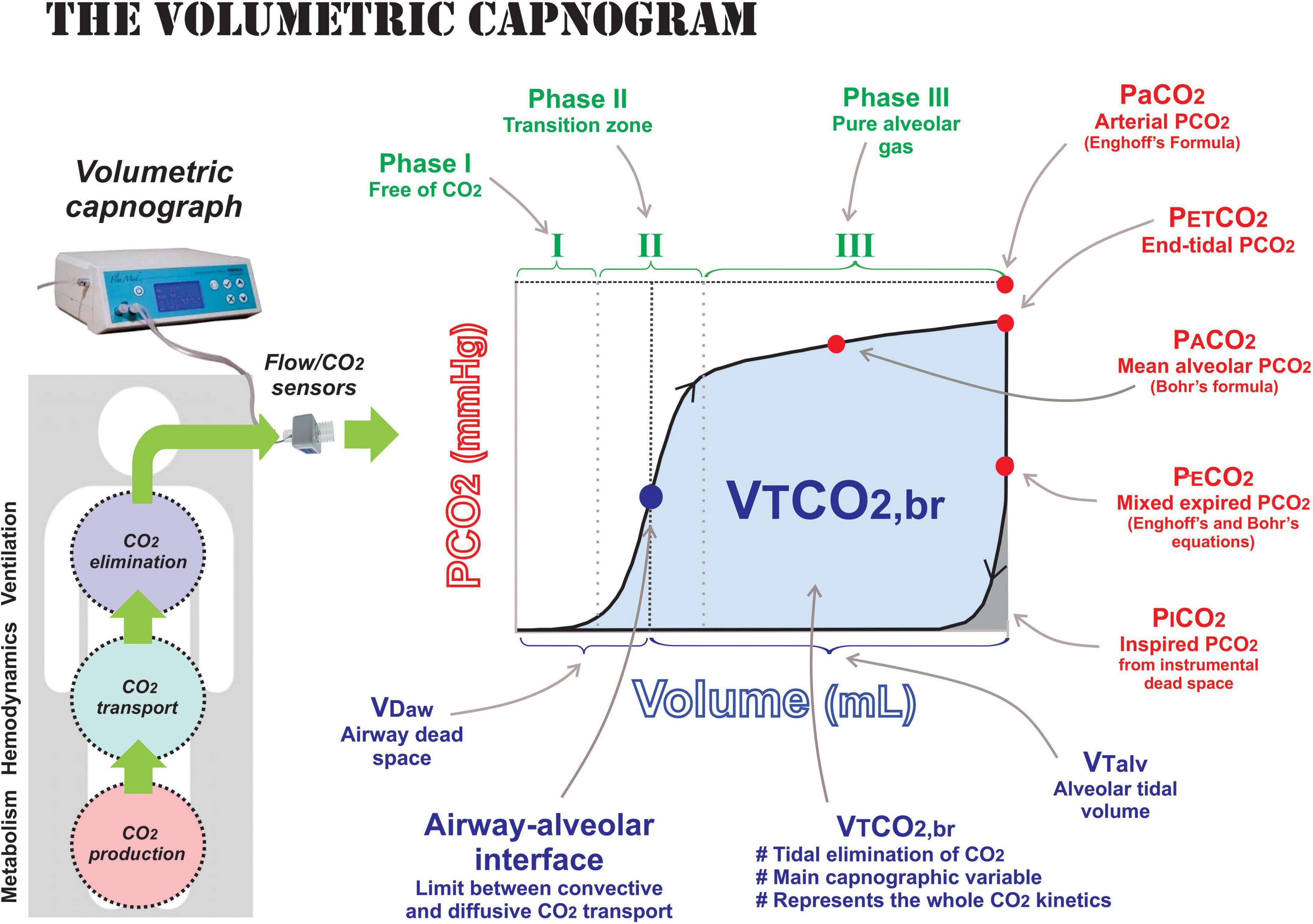
Tidal volume is the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle. The volume of air can refer to tidal volume (the amount inhaled in an average breath) or something more specific, such as the volume of dead space in the. Cpap produces an increase in tidal volume with a subsequent reduction in the work of breathing.
Although possible, actual tidal volumes in the range of 7·5 ml/kg of predicted bodyweight (assuming dead space of around 2 ml/kg of bodyweight) are unlikely to lead to. In addition, look at the tidal volumes the patient is getting. The amount of inspiratory pressure will vary based on the compliance of the patient’s lungs.
It’s possible that higher tidal volumes reflect more dysfunction lungs (greater dead space), which requires patients to take bigger breaths to clear co2.